July 27, 2022 by Marjorie R. Rogers, MA (English), Certified Consultant
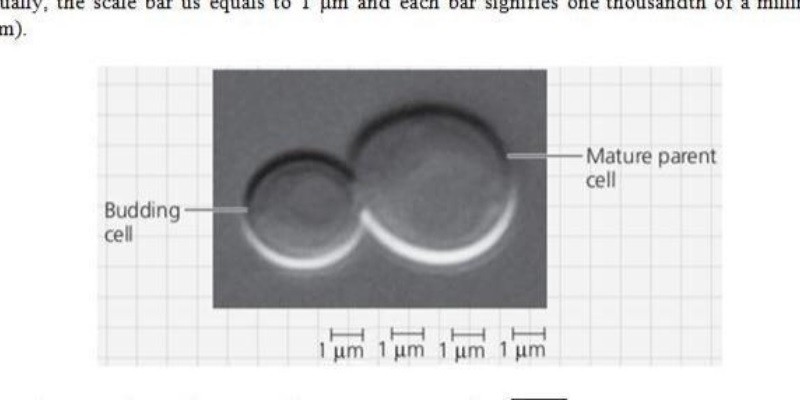
The average diameter of a mature parent cell is about 10 micrometers. The range can be from 4 to 20 micrometers. The larger the cell, the greater the risk of developing cancer.
The smaller the cell, the greater the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
The mature parent cell is approximately the same diameter as the original cell. The cell wall of the mature parent cell is thick and strong, and the cell membrane is also thick and strong. The cell is filled with a variety of organelles, including the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes.
There is also a large amount of cytoplasm in the cell.
Credit: www.alamy.com
What is the approximate diameter of the mature plant cell?
The mature plant cell has an approximate diameter of 20-30 micrometers. The cell wall is about 10 micrometers thick, and the plasma membrane is about 7 micrometers thick. The vacuole is the largest organelle in the plant cell, and can take up 50% or more of the cell’s volume.
What is the approximate diameter of a membrane?
A membrane is a thin layer of material that separates two environments. The most common type of membrane is a cell membrane, which separates the contents of a cell from the outside environment.
The diameter of a membrane varies depending on the type of membrane.
For example, the cell membrane is only about 7 nm thick, while the nuclear membrane is about 10 times that thickness at around 70 nm.
When the budding cell matures it will be approximately how many times greater in volume and how many times greater in surface area than its current size?
A cell will typically increase in size by a factor of two when it matures. This means that the mature cell will be twice as large in volume as the current cell, and will have twice the surface area.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the volume of mature plant cells taken up by vacuoles?
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that are found in all plant cells. They vary in size and number depending on the plant cell type and stage of development. However, all vacuoles have one common function: to store water and other materials.
The volume of mature plant cells taken up by vacuoles can vary depending on the cell type and stage of development. For example, guard cells which surround stomata (pores in the leaves through which gas exchange occurs) are typically smaller and have fewer vacuoles than other types of plant cells. This is because guard cells need to be able to change shape quickly in order to open and close the stomata.
On the other hand, cells in the root system tend to be larger and have more vacuoles than other types of plant cells. This is because roots need to store a lot of water in order to support the plant.
In general, the volume of mature plant cells taken up by vacuoles increases as the plant matures.
This is because vacuoles play an important role in plant growth and development. As the plant grows, more vacuoles are needed to store water and other materials. Additionally, vacuoles help to keep the plant cell rigid.
Without vacuoles, plant cells would collapse due to their own weight.
So, to answer the question, the volume of mature plant cells taken up by vacuoles can vary depending on the cell type and stage of development. However, in general, the volume of mature plant cells taken up by vacuoles increases as the plant matures.
MEGAKARYOPOIESIS PART 1
Which of the following statements about the nuclear envelope is false?
The nuclear envelope is a membrane that surrounds the nucleus of a cell. It is made up of two layers of membrane, the inner and the outer nuclear membrane. The nuclear envelope is important in keeping the contents of the nucleus separate from the rest of the cell.
One of the main functions of the nuclear envelope is to act as a barrier between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. This barrier helps to keep the genetic material of the nucleus safe and intact. The nuclear envelope also helps to regulate the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
The nuclear envelope is made up of two layers of membrane, the inner and the outer nuclear membrane. The inner nuclear membrane is continuous with the nuclear pores, which are tiny openings that allow materials to pass in and out of the nucleus. The outer nuclear membrane is connected to the endoplasmic reticulum.
The nuclear envelope is important in keeping the contents of the nucleus separate from the rest of the cell. However, it is not a perfect barrier. Some materials, such as RNA and proteins, can pass through the nuclear pores.
Conclusion
The average diameter of a mature parent cell is about 10 micrometers. This can vary depending on the type of cell, but most cells are around this size.
About Author (Marjorie R. Rogers)
The inspiring mum of 6 who dedicates her time to supporting others. While battling with her own demons she continues to be the voice for others unable to speak out. Mental illness almost destroyed her, yet here she is fighting back and teaching you all the things she has learned along the way. Get Started To Read …